What is nothing? What comes to mind when you imagine nothing? The moment we try to imagine what nothing is, we fail, because nothing cannot be envisioned. There is nothing to envision or ponder or even think about. Nothing is no thing.
Yes, the point above is tedious, but the value of nothing in the financial theater is the latest magic trick of the central bankers and the most vital factor governing all investments.
If I invest my hard-earned capital in an asset the guarantees a return of nothing, what should I expect as a return? Nothing is a good answer, and somewhat absurdly, there is the possibility that nothing is the best-case scenario.
Let’s take it one step further to beyond nothing. In the current age of financial alchemy, there is nearly $15.5 trillion in sovereign and corporate bonds available that promise a return of not only nothing but actually less than nothing.
If I am hired to steward capital and I invest in something that returns less than nothing, I have knowingly given away some portion of the capital I invested, and I should find another profession.
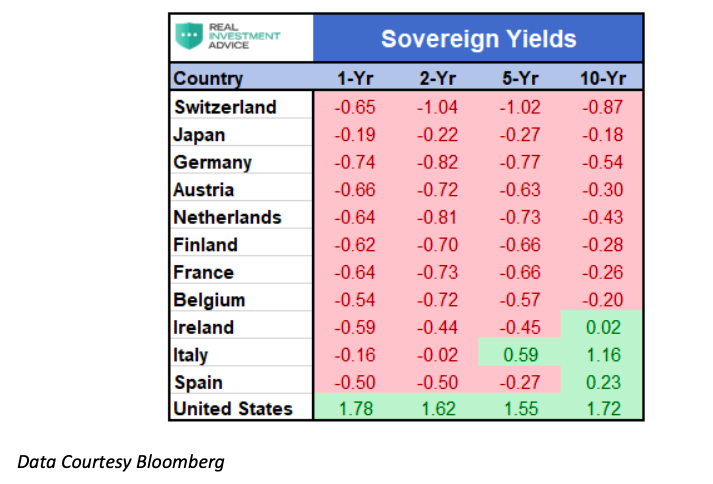
And yet, on this very day, there are trillions of dollars’ worth of bonds that promise a return of less than nothing. Furthermore, there are many professional investors who knowingly and willingly are buying those bonds! The table below shows the many instances of negative-yielding sovereign bonds, with U.S. yields as a comparison.
Warped Logic
The discussion and table above highlight just how far astray the financial system has gone in Europe and Japan. What we are witnessing is not just coloring outside the lines; it is upside down and inside out. Central bankers are frantically turning cartwheels to convince us that current circumstances, though deranged and highly abnormal, are perfectly sane and normal. More often than not, politicians, the media, and Wall Street fail to challenge these experiments and worse generally echo the central bankers’ siren song.
How do investors conclude that there will be only good outcomes as a result of what are imprudent and illogical decisions and actions? Is it prudent to expect a bright future when the financial system punishes prudent savers who are most able to invest in our future and rewards ill-advised borrowing beyond one’s means?
The current market and economic environment beg for lucid evaluation of circumstances and intelligent, honest discourse on the potential implications.
Unfortunately, most market participants would prefer to keep their head in the sand. Chasing the stock and bond markets for the past decade has produced handsome returns and, for most investment advisors, delivered praise and a generous wage. As Upton Sinclair said, “It is difficult to get a man to understand something when his salary depends upon his not understanding it.”
Compounding wealth is the most important and most difficult financial concept for investors to grasp. Over the last ten years, many investors spent significant time recouping losses from the financial crisis, and they assumed great risk in doing so. Having recovered some or all of those losses, many are back in a position of compounding wealth.
At this point, they can continue to look backward and believe that irrational policies will ensure that the past is prologue, or they can exercise some independent thought and recognize that the risk of another serious drawdown is not negligible. Prudent risk management is very generous to those who elect patience over expedience. Most financial advisors will not volunteer a fee-reducing, conservative approach even though it would be in their own best interest to do so at critical times.
Entities empowered with the responsibility of directing traffic and ensuring againstbad behavior that wish to “manage” markets are increasingly weighed and found wanting. They have become a part of the bad behavior they were entrusted to prevent, yet again. Actions, or the lack thereof, that resulted in the destruction of wealth in recent history have been on full display for over the past decade. However, with stock markets near record highs today, these actions (or inactions) are cloaked in an artificial façade of success.
Retrospect
It has become cliché to point back to October 1929, the dot.com bubble, and the housing bubble as a reminder of what may transpire. Bulls confidently look at the bears citing those periods, just as Monty Python’s King Arthur looks at the Black Knight after dismembering his arms and legs and says, “What are you going to do, bleedon me?”
Yet, historical episodes arethe correct frame of reference. Just as in those prior bubbles, the problem today is right in front of our face. The evidence is clear and the lunacy unmistakable. The poster child in 2000 was Pets.com and the sock puppet; in 2006 it was skyrocketing home prices and negatively amortizing subprime “liar” loans. Today, it is negative interest rates.
It is not hyperbole to say that today’s instance of finance gone wild is more insane than Pets.com, neg-am liar loans and any other absurd Ponzi scheme that has ever been perpetrated, ALL PUT TOGETHER.
The dot.com market collapse cost the economy roughly $8 trillion. The estimate of the cost of the 2008-09 financial crisis is $22 trillion. The market value of debt outstanding with negative interest rates is over $15 trillion.
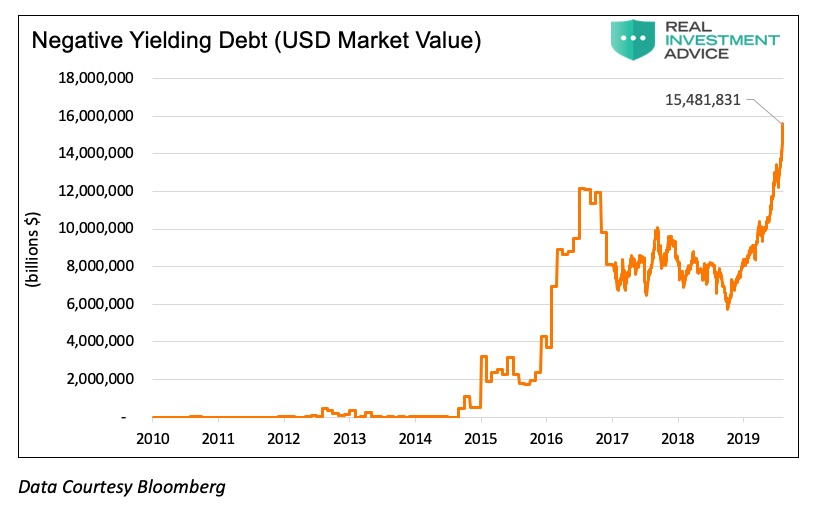
Although $15 trillion is less than the financial crisis losses, what must be considered is the multiplier effect. The losses in prior recessions were in part caused by the factors listed above but magnified by their ripple effect on other aspects of the economy and financial markets. This is the multiplier of the cause or the epicenter. Consider the following:
- The S&P 500 Information Technology sector market cap was roughly $4 trillion in March 2000. The total market losses from the tech bubble amounted to about $8 trillion; therefore, the damage in that episode was about $2 for every $1 of exposure ($8T losses vs. $4T exposure) to the epicenter of the problem, so the multiplier was 2:1.
- The toxic sub-prime part of the mortgage market was about $2 trillion. So, the impact of losses was $11 for every $1 of exposure ($22T loss vs. $2T exposure) to the epicenter, or a multiplier of 11:1.
- If a problem emerged today and we are correct that the epicenter of this problem, negative-yielding debt, is further reaching than those prior mentioned episodes, then using a simple 11-to-1 ratio on $15 trillion is $165 trillion in losses, may be understating the potential problems. Even being very conservative with a 2:1 multiple yields mind-boggling losses.
This is unscientific scenario analysis, but it does provide a logical and reasonable array of possible outcomes. If one had postulated that the sub-prime mortgage market would spark even $2 trillion in losses back in 2007, they would have been laughed out of the room.
Some people did anticipate the problem, made their concerns public, and were ridiculed. Even after the problem started, the common response was that sub-prime is too small to have an impact on the economy. In fact, the Fed and other central banks stood united in minimizing the imminent risks even as they were wreaking havoc on the financial system. Likewise, the “scientific” analysis currently being done by Ph.D. economists will probably miss today’s problem altogether.
European Banks
The concept of negative-yielding debt is totally irrational and incoherent. It contradicts every fundamental rule we learn and attempt to apply in business, finance, and economics. It implies that the future is more certain than the present – that the unknown is more certain than the known!
When the investment/lending hurdle rate is not only removed but broadly disfigured in how we think about allocating resources, precious resources will be misallocated. The magnitude of that misallocation depends on the time and extent to which the policy persists.
As brought to our attention by Raoul Pal of Global Macro Investor and Real Vision, the first evidence of problems is emerging where the negative interest rate phenomenon has been most acute – Europe. European financial institutions are growing increasingly unhealthy due to the damage of negative rate policies.
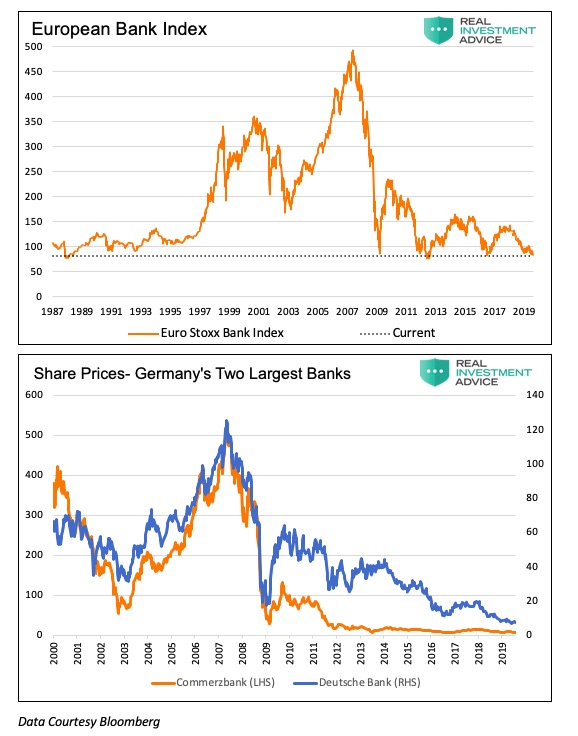
Currently, the Euro STOXX Bank index, as shown below, trades at levels below those of the trough of 2009 and its lowest levels since 1987. More importantly, the index is on the verge of breaking through a vital technical level to the downside. The shares of Germany’s two largest banks, Deutsche Bank and Commerzbank, are at historical lows. Just as subprime was not isolated to the U.S., this problem is not isolated to Europe. These banks have contagion risk that, if unleashed, will spread throughout the global financial system.
Summary
The market is reflecting a growing lack of confidence in the European banking and financial system as telegraphed through stock market pricing shown above.
The risk facing the global financial system is that, as problems emerge, the second and third-order effects of those issues will be both impossible to anticipate and increasingly difficult to control. Trust and confidence in the world’s central bankers can fade quickly as we saw only ten years ago.
Compounding wealth depends upon minimizing the risk of a large, permanent loss. If markets falter and the cause is monetary policy that advocated for negative interest rates, investors will have to accept accountability for the fact that it was staring us in the face all along.
Twitter: @michaellebowitz
Any opinions expressed herein are solely those of the author, and do not in any way represent the views or opinions of any other person or entity.